The cosine law is a trigonometry law which can be used to derive the missing lengths of sides and angles of corners in triangles based on the lengths and angles of known sides. To do this, it requires knowledge of the lengths of at least 2 sides of the triangle, and either a known length of the third side, or the angle of the corner between the length of the known sides. Like with other trigonometric laws for non right triangles, this law defines the sides using the lowercase letters a, b and c and corners as uppercase letters A, B and C (Figure 1).

There are two applications of the cosine law, and it is simpler to express these are different formulae. However these two equations are rearrangements of the same law, and the equation that defines them. These different equations can be used to determine the length of a missing side (c) or the angle of a missing corner (C), given the length of two other sides (a and b) and the side (c) or corner (C) opposite to the one being determined. In the cosine law equations, the lengths of sides a and b are interchangeable, as long as they are the two sides adjacent to the corner specified as C, while side c and corner C are always the side or corner of interest.
$$c^2=a^2+b^2-2ab\cos C$$
$$\cos C = {a^2+b^2-c^2 \over 2ab}$$
Cosine Law for a Missing Side
The cosine law can be used to find the length of a missing side if the lengths of the other two sides are known, along with the angle between them (Figure 2).
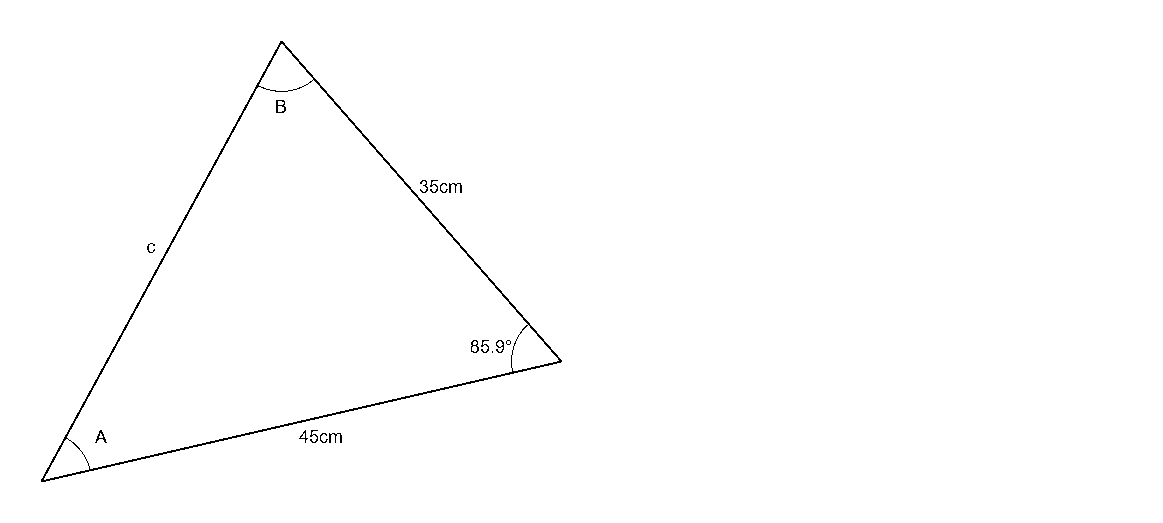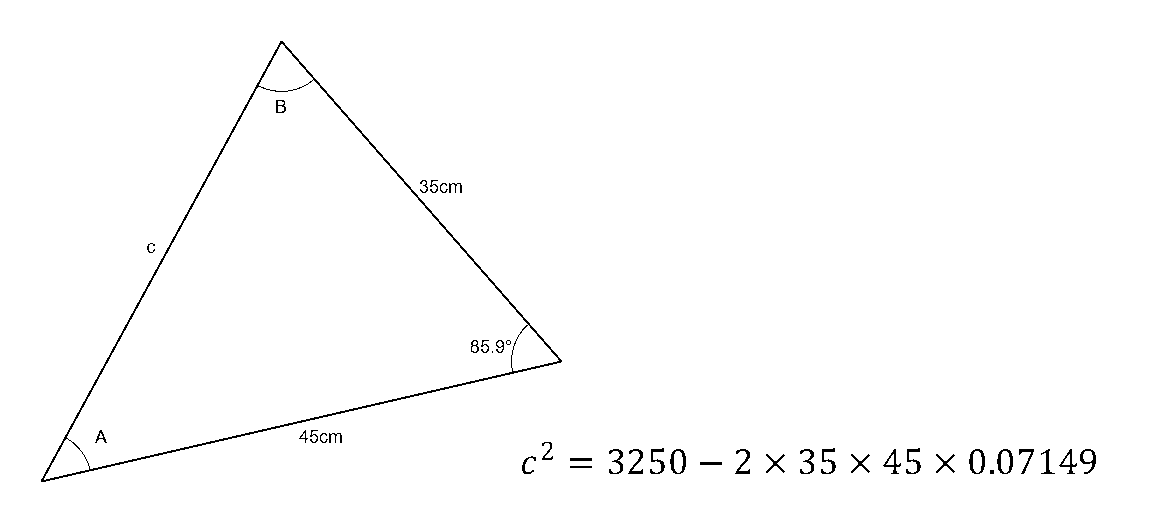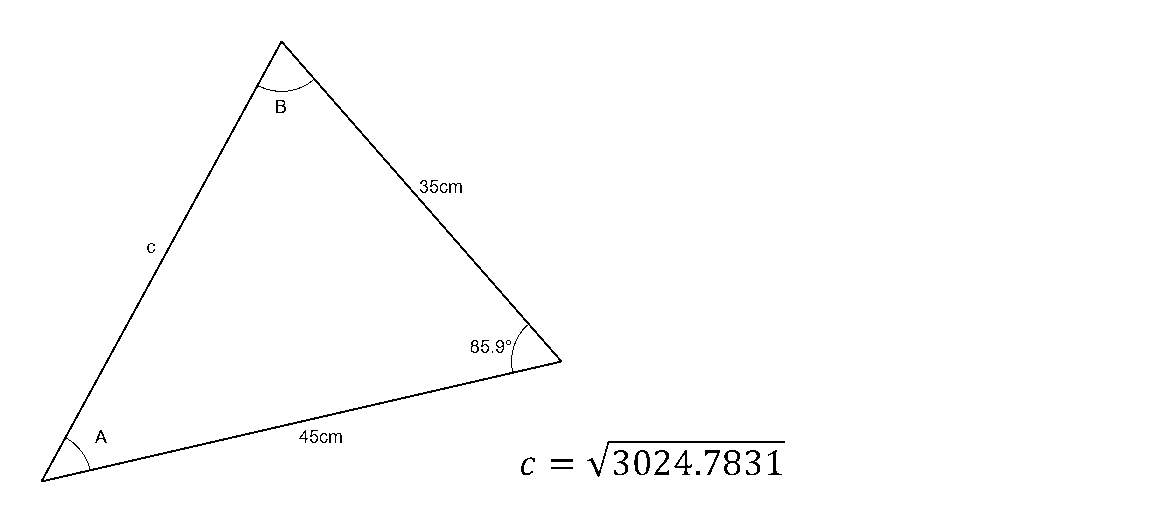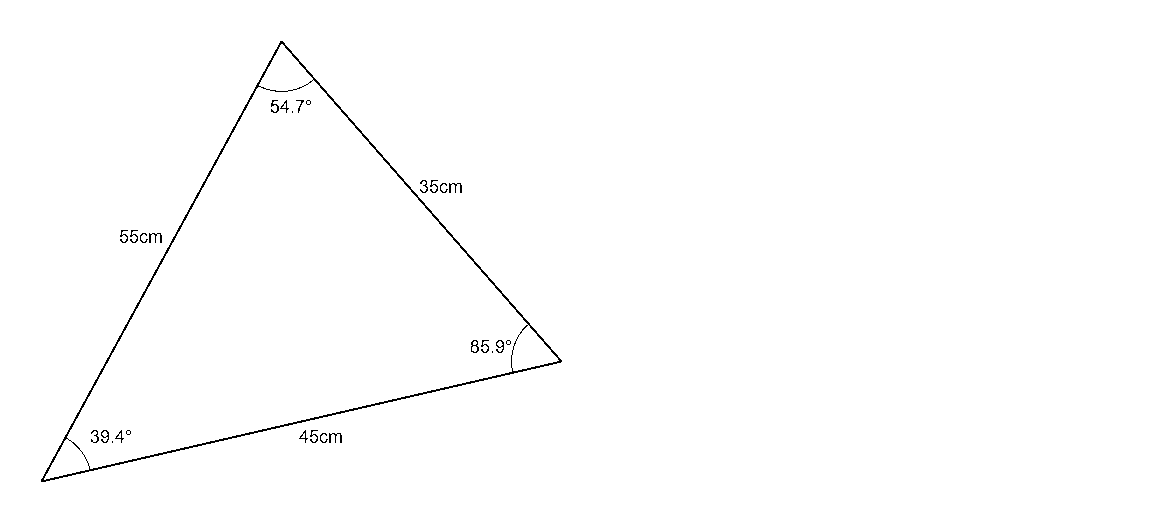
To do this the lengths of the known sides and the angle of the known corner are substituted into the cosine law equation for the length of a side. The length of the side being calculated is always defined as c, and the angle of the known corner opposite this side is always defined as C. The other two known sides are substituted into the equation as a and b. It doesn’t matter which side is substituted into the place of each letter, they are interchangeable and are treated the same by the equation.
$$c^2=35^2+45^2-(2\times35\times45\times\cos85.9)$$
As the equation is for the square of the side c, taking the square root of both sides will find the length of side c and thus solve the length of the triangle using the cosine law.
$$c=\sqrt{35^2+45^2-(2\times35\times45\times\cos85.9)}$$
Cosine Law for a Missing Corner
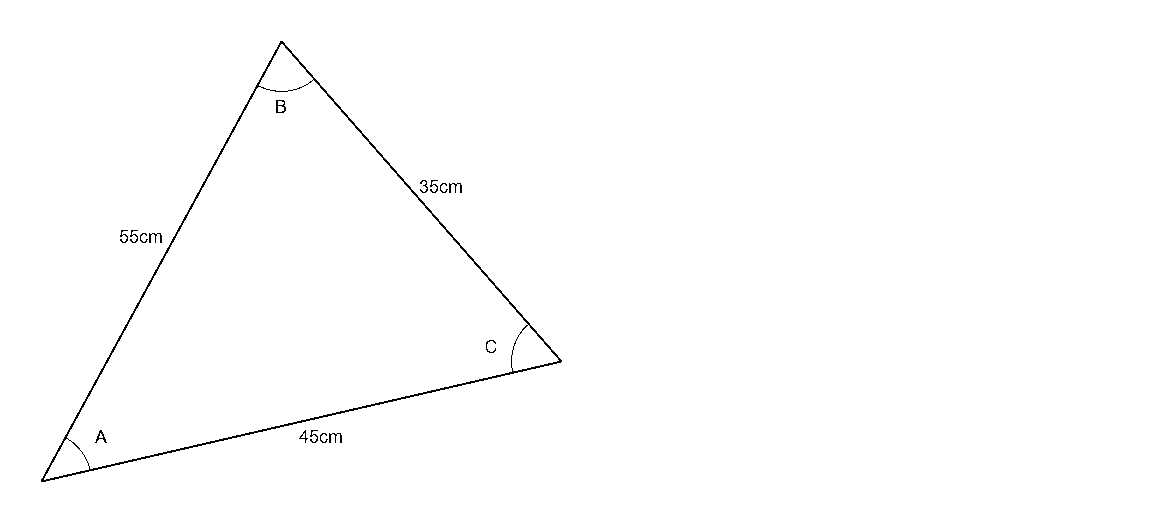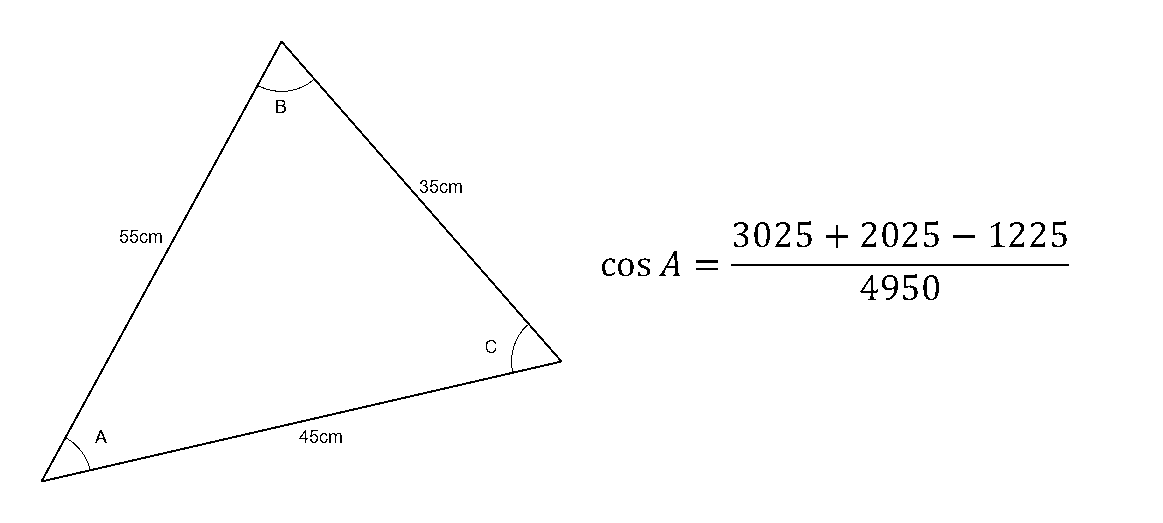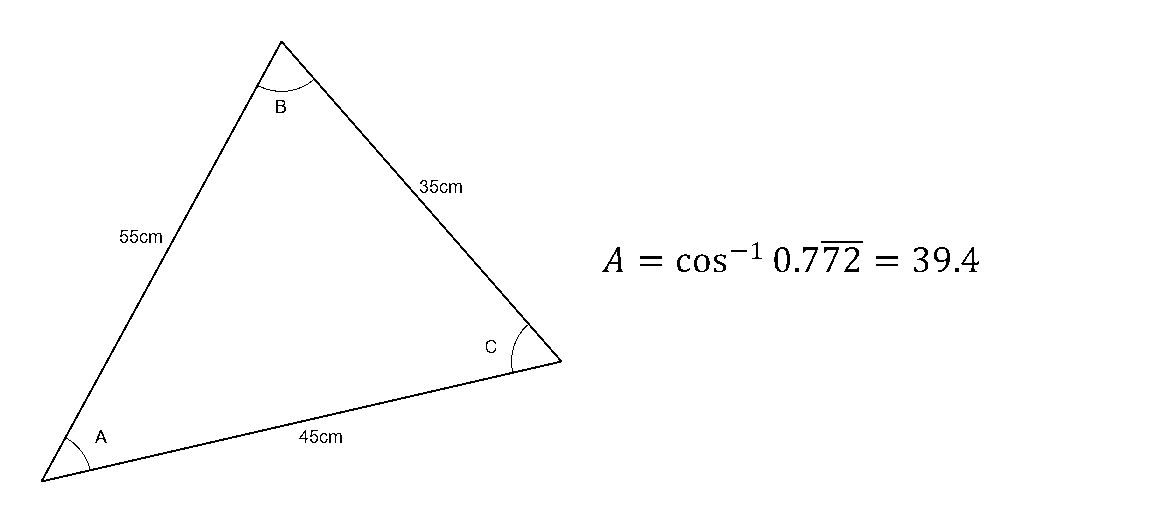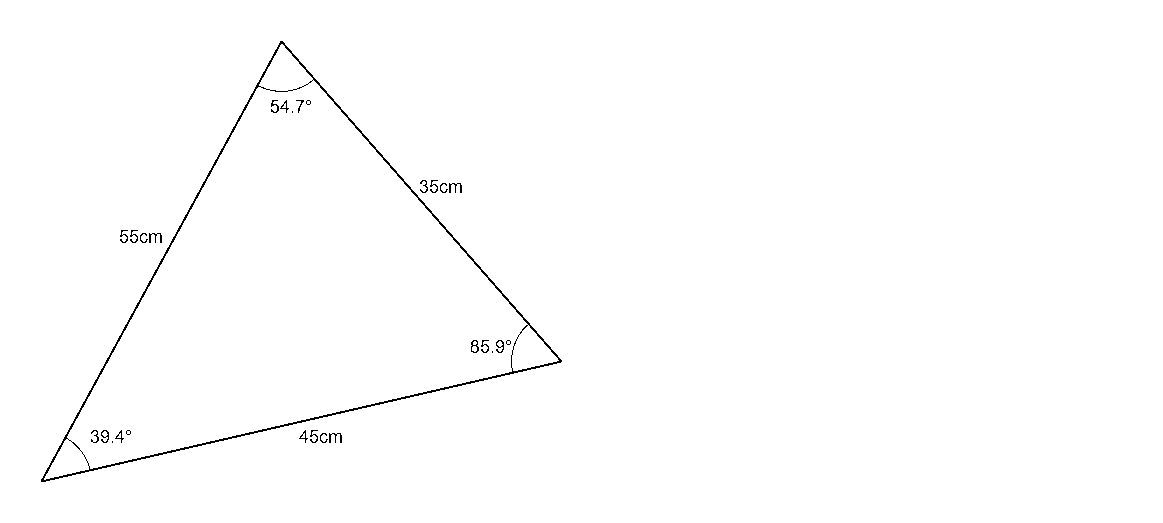
If the lengths of three sides of a triangle are known, the cosine law can be used to find the angle of any corner in the triangle (Figure 3).
In this case, the lengths of the sides in the triangle can be substituted into the cosine law equation. The angle being solved is the angle of corner C, and the length of the side opposite this corner is defined as c. Like with the side law for the length of a side, the lengths of the other two sides are substituted as a and b, and these two values are interchangeable in the equation.
$$\cos C={{35^2+45^2-55^2}\over{2\times35\times45}}$$
As the equation is for the cosine of angle C, we can apply the inverse cosine function, cos^-1 to both sides of the equation, to give the equation for the angle at corner C.
$$C=\cos^{-1} ({{35^2+45^2-55^2}\over{2\times35\times45}})=85.9$$